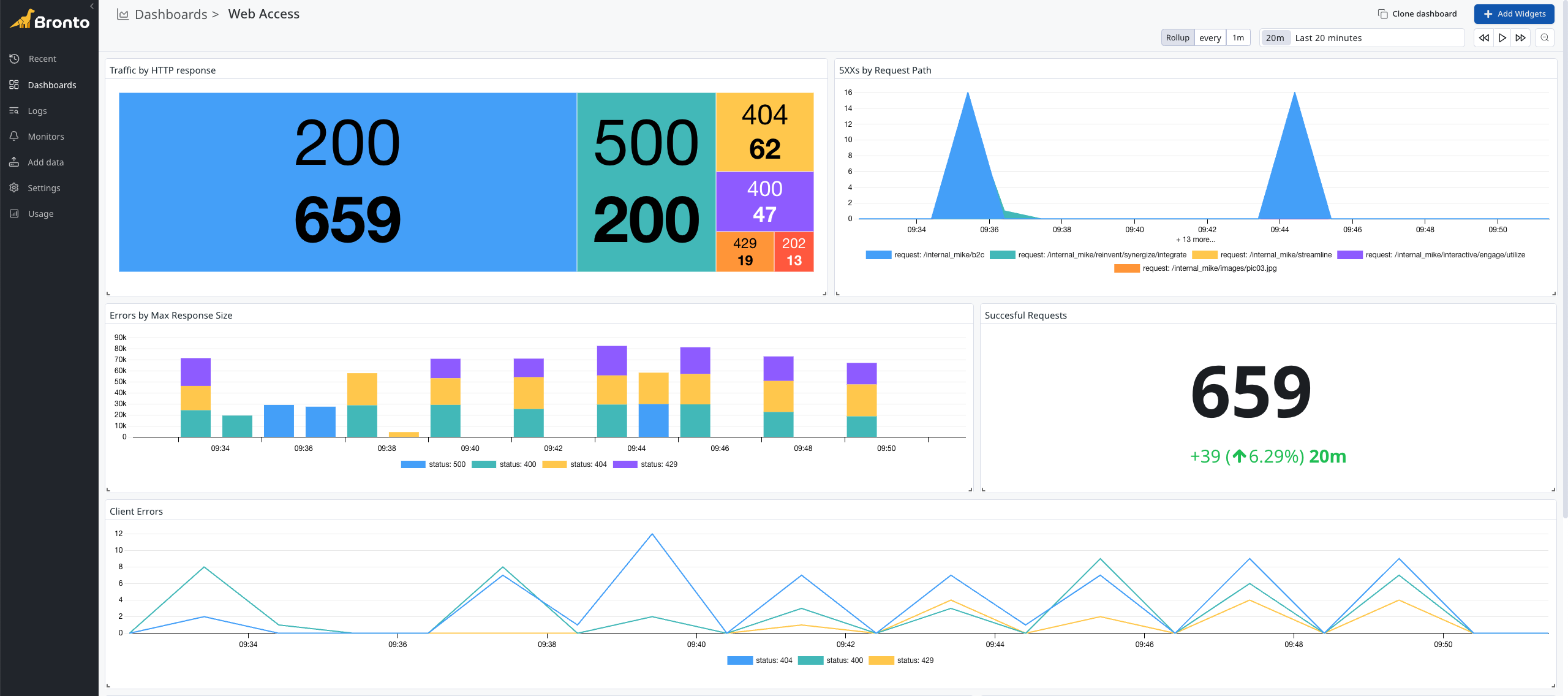
Dashboards
Bronto dashboards are a powerful way to visualize your log data and gain insights into your application's performance. Dashboards are driven by log based metrics, which are calculated based on the log data you have ingested.
Overview
Navigate to the Dashboard page in Bronto by clicking on the "Dashboards" item in the application sidebar.
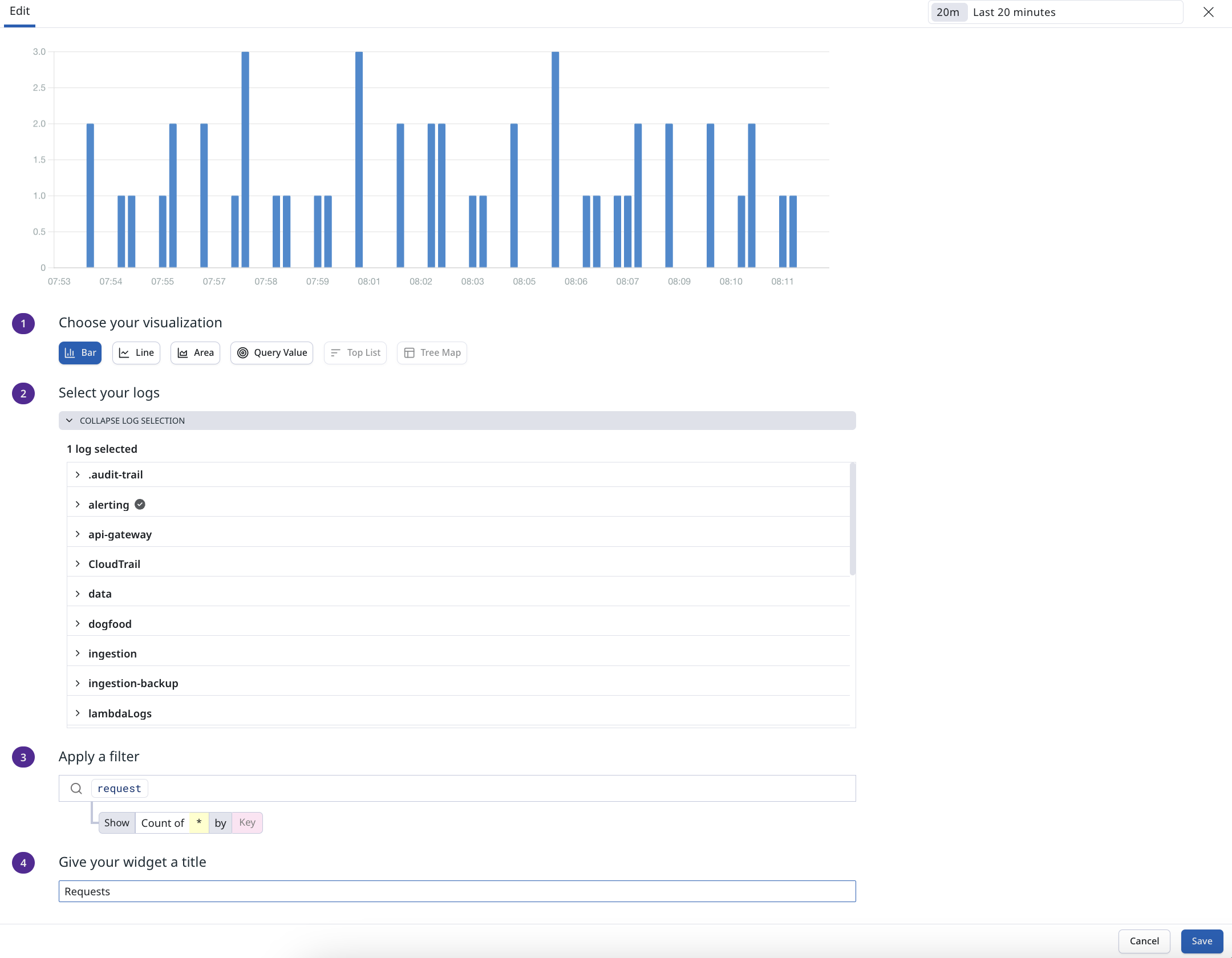
Create a new Dashboard
To create a new Dashboard, click on the "New Dashboard" button in the application sidebar
- Choose a name for your Dashboard
- Once the dashboard is created, click Add Widgets
- Choose a visualization type for your metric (e.g. Bar, Line, Area, Query Value, Top List or Tree Map)
- Select the logs you want to associate to the widget
- Apply a filter, for more details see the Query Syntax help page
- Lastly give the widget a title and select Save. Save up to 50 widgets per dashboard
Visualization Types
Visualization types are the various charts you can include in your widget to display your data.
Bar Graph
A bar graph is a visual representation of data that helps to analyze and interpret the frequency, volume, or other metrics associated with your data. Example uages would include showing error frequency over time, log volume by source and types of logs (info, error or warning).
Line Graph
A line graph is a graphical representation of information that changes over a period of time. It is a chart made by joining points using line segments.Line graphs are particularly effective for showing trends and patterns over a continuous period. They are ideal for understanding how log metrics change over time. Example usage would include error rates over time, log volume over time and displaying response times.
Area Graph
An Area Graph is a visual representation of data that utilizes both lines and filled areas to convey information over a period of time. This type of chart is particularly effective in showcasing data trends and variations over a specified period or across different categories.
Query Value
This widget can display the latest value from your various search queries across a specific time window.
Top List
The top list visualization enables you to display a list of search values with the most or least of any metric or event value. Examples include graphing cpu usage, disk space or costs of particular services.
Tree Map
Tree maps are used to represent hierarchical data as nested rectangles. They help in understanding the structure and distribution of data within a hierarchy. Examples include log volume by source and type, error distribution across services, resource allocation, and other hierarchical metrics.
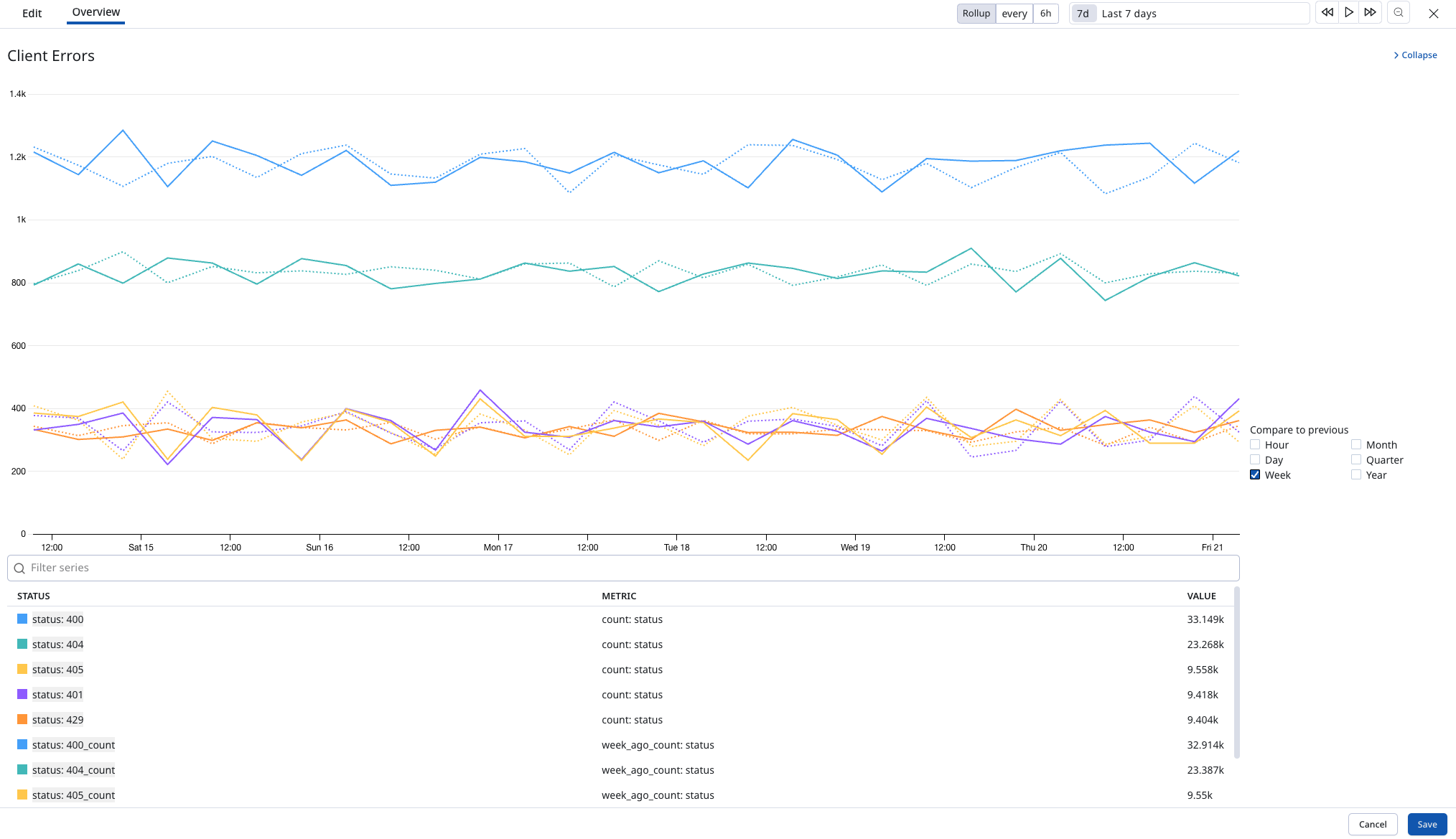
Percentiles
Analyse your data with percentile views, including P75, P90, P95, and P99, for deeper insights into performance and trends.
Full Screen Mode
In full-screen widget mode, when using bar, line, or area visualizations, you can now chart and compare previous time periods by days, weeks, months, or years.
The full-screen mode toggle is located in the top right of each widget, next to the edit options. You can also select or deselect keys to customize the data displayed on the graph.